Digital Competence of Educators
The digital world is a new space for interaction, learning and development in today’s society. For this reason, it is essential that we as teachers become aware of the European recommendations regarding key competences for lifelong learning, since, for teachers, the development of digital competences is not only the domain of devices and applications; it also involves the responsibility of using them in a pedagogical fashion. This approach advocates the need to keep inclusion in mind, so that digital technologies are accessible to all students. In addition, it encourages collaborative work, respect for people and the environment, and a responsible, critical and safe use of technology. Likewise, it ensures the preservation of social and family privacy, and the protection of personal data, among many other aspects.
To act in accordance with the needs of society in general, and of education in particular, we must acquire an increasingly broad set of competencies and strategies in our teaching so as to adapt to the new pedagogical tools that the digital age has to offer. This situation acknowledges the need for a document such as the Common Digital Competence Framework for Teachers, which serves as a guide in the process of acquiring these new skills.
Common Digital Competence Framework for Teachers
The Common Digital Competence Framework for Teachers (CDCFT) is a reference guide that adapts the European Framework for the Digital Competence of Educators (DigCompEdu) to the Spanish context. Written and published by the Joint Research Center (JRC) of the European Commission and translated into Spanish by the National Institute of Educational Technologies and Teacher Training (INTEF).
The DigCompEdu document provides a common approach for all the professionals dedicated to teaching at all educational levels, from early childhood education to higher and adult education, which zeros in on general and vocational training, students with specific needs and any other non-formal learning environments.
The goal of the CDCFT is to determine, according to the Organic Law of Education, which digital competences any formal education teacher must achieve and develop, regardless of the area, subject, stage or type of teaching, to acquire teaching expertise in relation to the different areas that this framework establishes.
It should be noted that, at the meeting of the Education Sector Conference on March 30, 2022, the Agreement to adapt the Common Digital Competence Framework for Teachers was approved by all the Autonomous Communities on May 14, 2020, in order to adapt it to the evolution of digital technologies and their educational use. The Agreement was made official through the Resolution of May 4, 2022, of the General Directorate of Evaluation and Territorial Cooperation, which published the Agreement of the Education Sector Conference to update the Common Digital Competence Framework for Teachers.
The schools that would like to certify and accredit the digital comeptence will have to meet some requirements and follow criteria that are included in the Resolution of July 1, 2022, of the General Directorate of Evaluation and Territorial Cooperation, which publishes the Agreement of the Sectoral Conference of Education on the certification, accreditation and recognition of the digital competence of educators.
Digital Competences
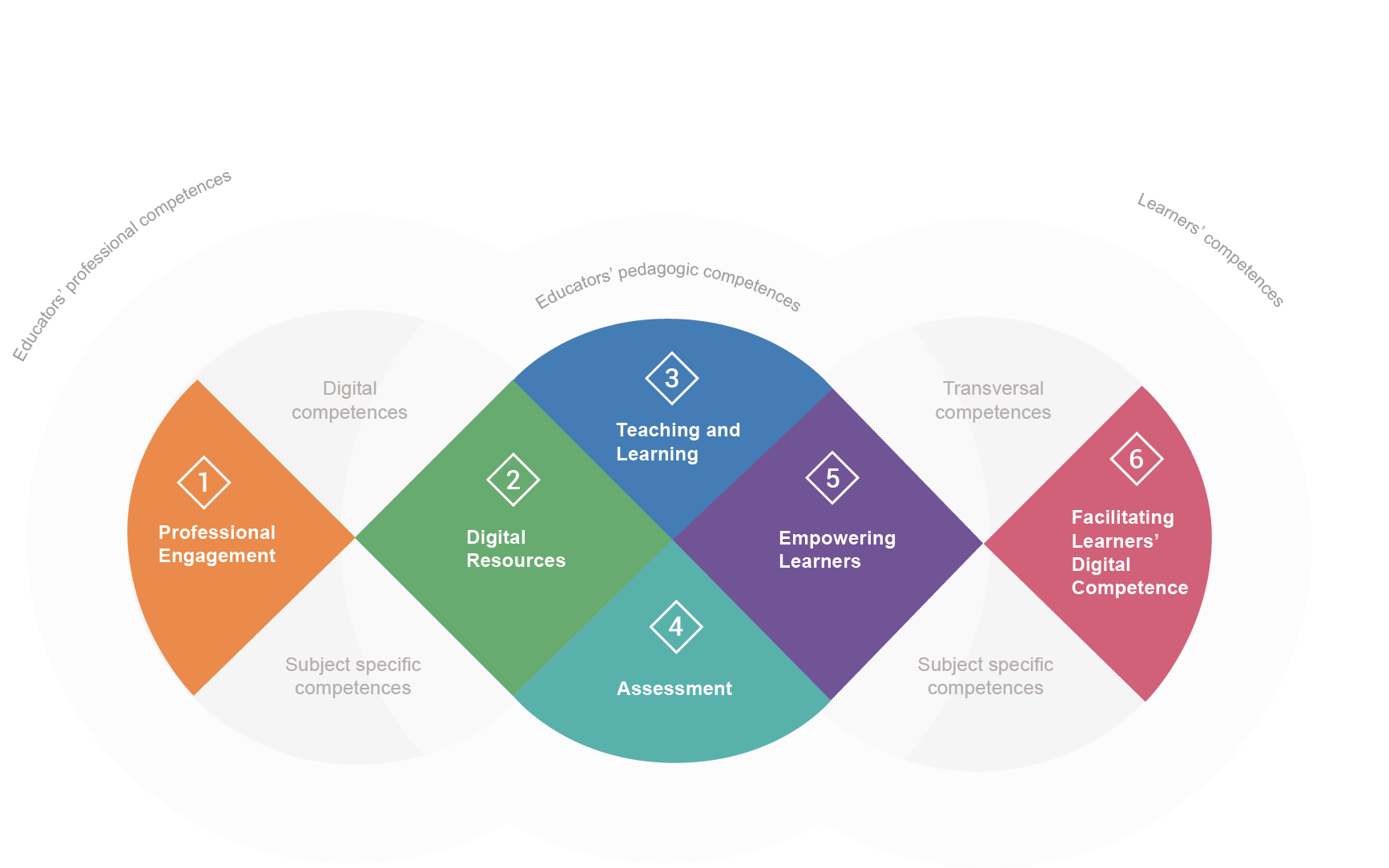
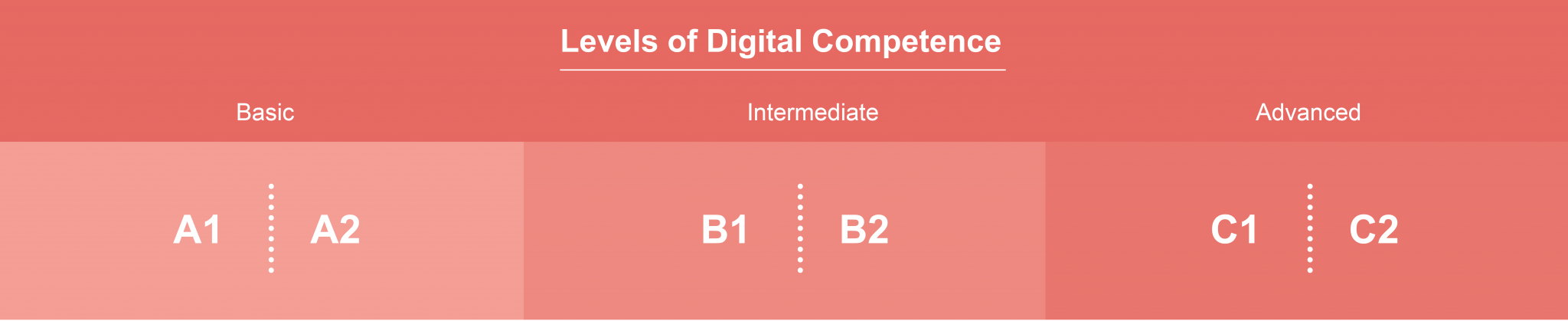
The CDCFT structures the teaching of digital competences in six areas, establishing a progressive level of development and autonomy that ranges from A1 to C2.
The Framework considers six different competences areas:
- Area 1 focuses on the professional environment.
- Area 2 on sourcing, creating and sharing digital resources.
- Area 3 on managing and orchestrating the use of digital tools in teaching and learning.
- Area 4 on digital tools and strategies to enhance assessment.
- Area 5 on the use of digital tools to empower learners.
- Area 6 on facilitating learners’ digital competence.
To find out more, click on the areas below: