| |
Hey Heeeey!!
I know it is FRI-YAY and we have a long weekend to catch up on things, such as, extracurricular activities, meeting friends, etc…but also TO REVIEW AND STUDY  . .
This is a summary of what we have been doing this week, remember? I have also added extra information that you can read if you want.
1. A powerpoint all about changing states
2. A poster of diferent properties of materials
Hope you find it useful guys!  
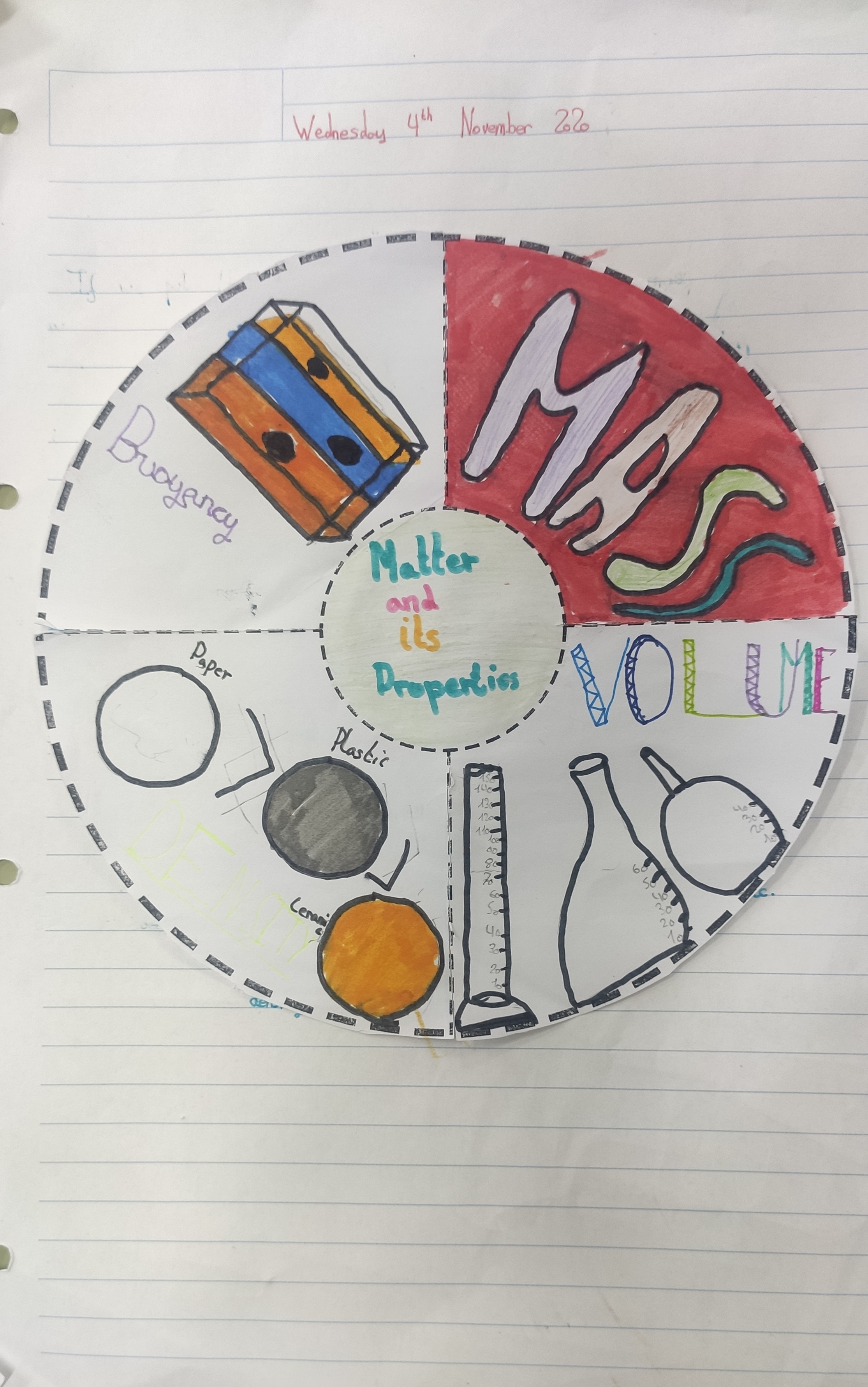
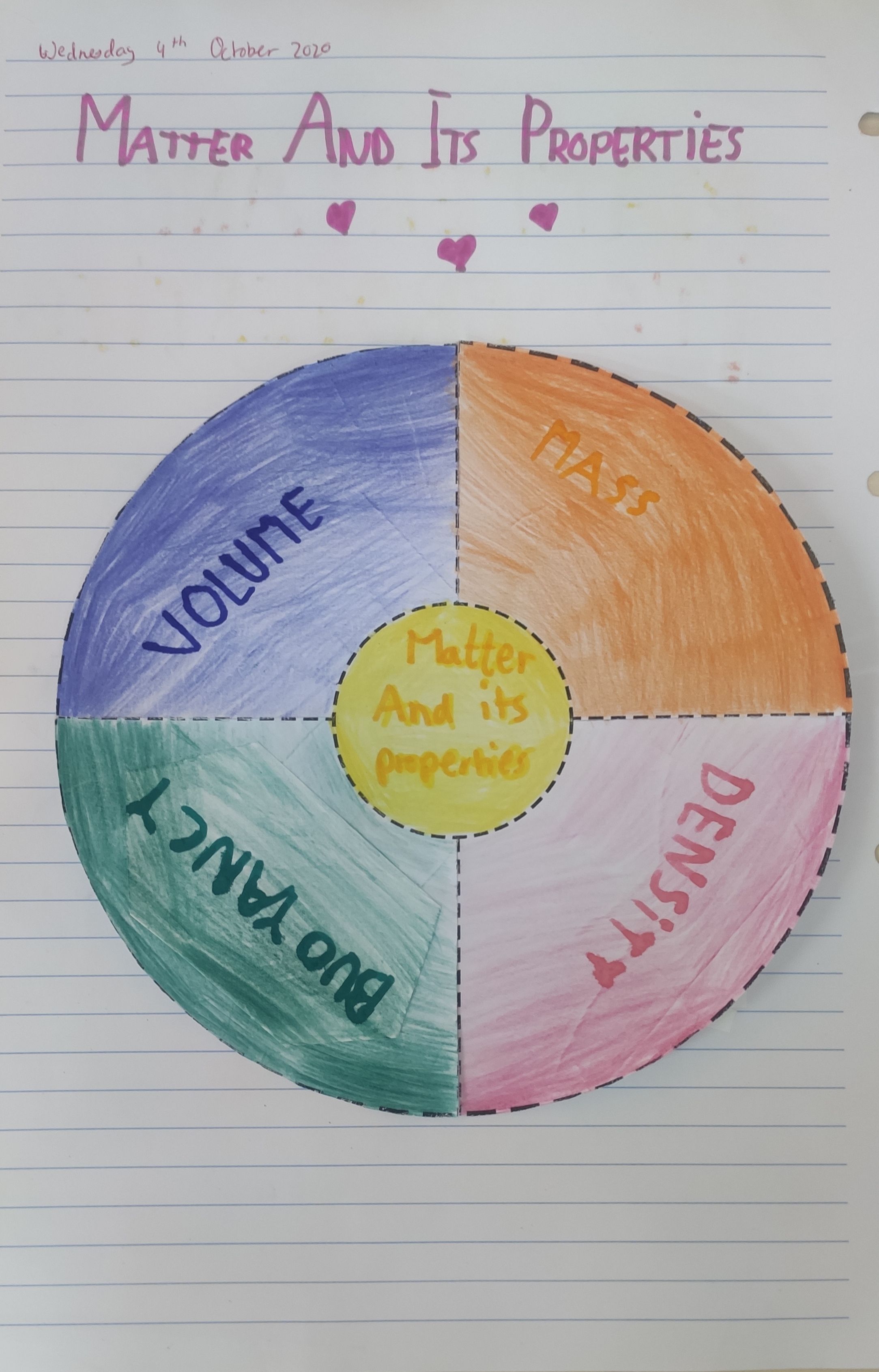
1. Matter and its properties
- All things are made of matter: our bodies, a notebook, a pen, a flower, the air, water, etc. A pen and water are different because they are different types of matter. Each type of matter is called a substance.
- An object’s mass is how much matter it has. For example, a notebook has more mass than a pen. To find an object’s mass, we have to weigh it. Mass is expressed various units, such as in grams (g) and kilograms (kg).
- An object’s volume is how much space it takes up. For example, a football has more volume than a tennis ball. The volume of liquid that a container can hold is its capacity. For example, a bottle has more capacity than a syringe. Volume is expressed in the liquid units of litre (L), centilitre (cl), millilitre (ml), etc.
- Objects can have the same volume, a different mass. This is because their density is different. To calculate an object’s density, we divide its mass by its volume.
- If we put the objects in water, we see that the iron object sinks, but the objects made of wood and cork float. An object floats or sinks in a liquid because of buoyancy. If the density of the object is less than that of the liquid, it floats. If its density is greater, it sinks.
2. Changes in matter
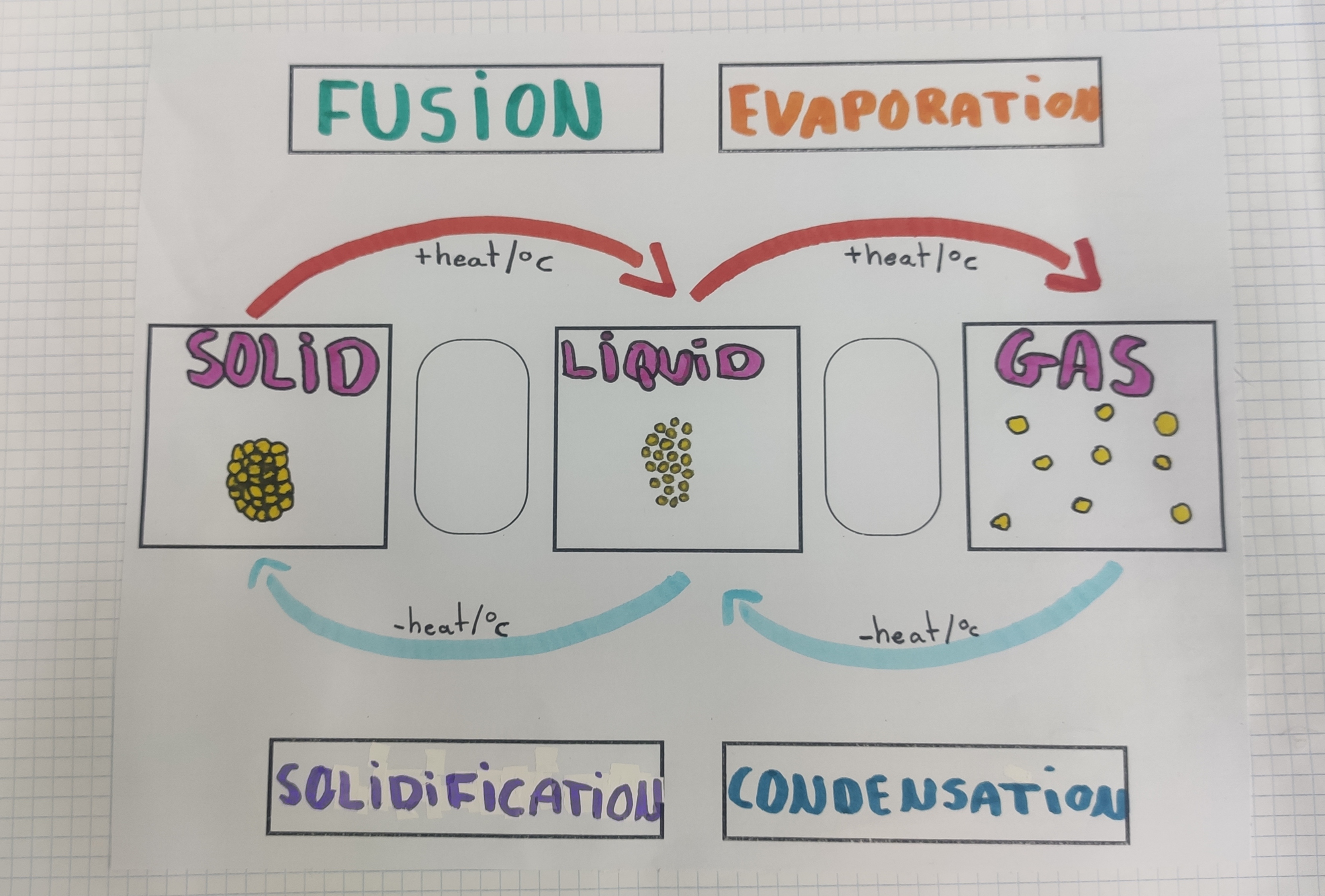
Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid and gas.
- The volume of solids does not change. However, if we can change the shape of a solid, we say
that it is malleable, like plasticine, or elastic, like rubber.
-
The volume of liquids does not change, but they change shape easily. Liquids take the shape of the container they are in.
-
The volume and shape of gases are always changing. Gases take the shape of the container they are in and fill its entire volume.
Matter can change its state when we apply a force such as increasing the temperature (heating) or reducing the temperature (cooling).
The main changes of state are:
-
Fusion (melting), the change from solid to liquid through heating.
-
Solidification (freezing), the change from liquid to solid through cooling.
-
Evaporation, the change from liquid to gas through heating.
-
Condensation, the change from gas to liquid through cooling.
Examples of common chemical changes:
-
– oxidation – when oxygen changes a substance into something else, as with the apple.
-
– combustion – when a combustible substance reacts with oxygen and produces gases (smoke), ash, light and heat.
|



 Anterior
Anterior 